AI-generated summary
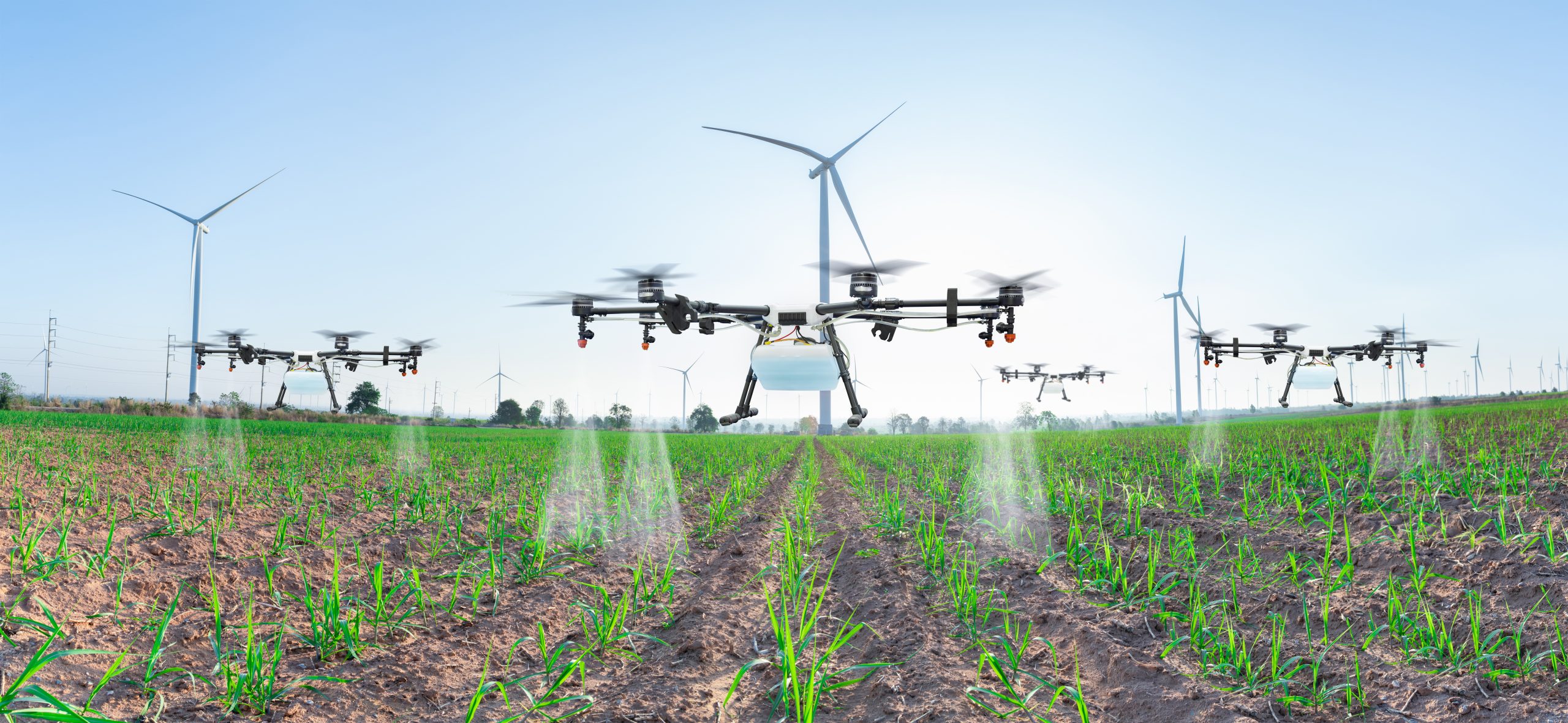
The Future Trends Forum, organized by the Bankinter Innovation Foundation in Madrid under the theme “Smart Agriculture: the Challenge of Sustainable Food,” gathered leading experts to explore the pressing issues of food security, sustainability, and innovation in agriculture. Miguel Calatayud, former CEO of iwi, highlighted the evolution of agriculture through the lens of water usage, emphasizing sustainability as essential for future production. He underscored water’s pivotal role amid climate change, desertification, and resource scarcity, advocating for precision irrigation and advanced technologies like artificial intelligence and big data to optimize water use and reduce environmental impact.
Calatayud also introduced innovative solutions such as cultivating microalgae in desert regions using saline water, a method that could transform unproductive lands into viable food sources while promoting social equity and economic revitalization in marginalized areas. This approach exemplifies how technology can democratize agriculture, expanding opportunities to communities affected by harsh environmental conditions and contributing to food sovereignty. Emphasizing water as a shared resource, Calatayud called for ethical and equitable management to ensure sustainable agriculture that supports both current and future generations, urging global commitment to innovation and responsible water stewardship for resilient food systems.
An analysis of how water management becomes the core of sustainable agricultural practices, with Miguel Calatayud
The think tank Future Trends Forum, under the slogan Smart Agriculture: the challenge of sustainable food, organised by the Bankinter Innovation Foundation in Madrid, has brought together leading experts and key figures in the field of agriculture and food. This event focused on examining current and future challenges related to food security, sustainability and innovation in the agricultural sector, underlining the critical role of emerging technologies and new methods to revolutionize these essential fields.
One of the participating experts was Miguel Calatayud, former CEO of iwi. In his presentation, he introduces us to the evolution of agriculture through its relationship with water, addressing from extensive and then intensive agriculture, and emphasizing sustainability as the cornerstone of future production.
If you want to see Miguel Calatayud’s presentation, you can do so in this video:
Miguel Calatayud: The evolution of agriculture through water
Calatayud explores how technology, especially artificial intelligence and big data, is accelerating the transformation towards more efficient and environmentally friendly practices. It invites us to reflect on the responsible use of resources and innovation in crops as key responses to the growing challenges in the agricultural sector, marked by climate change, water scarcity and biodiversity loss.
Water: the backbone of sustainable agriculture
In a world increasingly affected by climate change and the scarcity of natural resources, water is emerging as the central axis in the debate on agricultural sustainability. Miguel Calatayud’s presentation sheds light on this problem, highlighting how the agricultural sector is at a crucial crossroads, where efficient water management is a prevailing need. Calatayud underlines how the transition from extensive to intensive agricultural practices has increased the demand for water, putting the sustainability of the sector at risk. At this critical point, innovation emerges as the key to a greener future.
Current challenges: between scarcity and efficiency
The current scenario paints a picture where 20% of the Spanish surface is in the process of desertification, a phenomenon observable at a global level. This landscape transformation reduces the amount of arable land available and highlights the urgent need to adopt more water-conscious agricultural practices. Agriculture, being one of the world’s leading consumers of freshwater, faces the challenge of how to maximize productivity while minimizing its water footprint.
The role of technological innovation
Calatayud’s presentation highlights the transformative role of technology, especially in the implementation of precision irrigation systems. The adoption of technologies such as precision agriculture, based on data, allows for more efficient use of water, ensuring that every drop is used as effectively as possible. This approach reduces waste and boosts agricultural production, aligning cultivation practices with sustainability principles.
The importance of awareness and adaptation
Another crucial aspect that Calatayud emphasizes is the need for a change in mindset towards greater awareness of the value and importance of water. Sustainable water management requires technological innovations and adaptation in agricultural practices. This includes everything from selecting crops that are more resistant to drought conditions to cultivation methods that optimize water use, such as crop rotation, which benefits soil health and can reduce the need for extensive irrigation.
Towards a greener and fairer agriculture
Calatayud’s vision extends beyond water efficiency, embracing the idea of an agriculture that contributes to equity and social justice. It proposes the democratization of agriculture by introducing innovative crops, such as microalgae in deserts, using water with high salinity, which would otherwise be unusable for traditional agriculture. This approach opens up new opportunities for food production in drought-affected regions, which allows revitalizing communities and local economies through job creation and sustainable development.
Innovation in the desert: microalgae cultivation
Miguel Calatayud’s vision of agricultural innovation leads us to one of the most promising examples of how technology can transform challenges into opportunities: the cultivation of microalgae in desert areas. This approach addresses critical freshwater scarcity and arable land degradation, presenting a viable and sustainable solution for food production under adverse conditions.
Calatayud’s presentation illustrates how, in the context of increasing desertification and the urgent need for cultivation methods that conserve water resources, microalgae cultivation emerges as an innovative solution, using saline or high-salinity waters, which are abundant in desert regions, but traditionally considered inappropriate for conventional agriculture.
Microalgae cultivation: an alternative source of food
Microalgae, specifically the Nanochloropsis species, highlighted by Calatayud, are an underutilized resource with enormous potential for the production of nutrient-rich biomass. This type of algae can be grown in high salinity conditions and has the ability to grow rapidly, offering a sustainable source of protein, essential oils, and other valuable compounds. The productivity of microalgae, compared to traditional terrestrial crops, is astonishingly high, with the ability to produce significant amounts of essential amino acids per square meter, vastly outperforming other protein sources.
Growing microalgae in deserts has some challenges, including establishing adequate infrastructure and adapting culture techniques to extreme conditions. However, the potential benefits of this innovation far outweigh these obstacles. In addition to producing foods of high nutritional value, the cultivation of microalgae in desert areas represents a way to “democratize” agriculture, bringing food production to regions that have historically been marginalized in terms of agricultural resources.
Environmental and social impact
Environmentally, it represents an efficient use of otherwise unproductive land and water resources unfit for human consumption or traditional agriculture. Socially, it has the potential to revitalize local economies by creating new industries and employment opportunities in desert communities, thus contributing to more equitable and sustainable development.
In a world facing ever-narrowing ecological limits, innovation in growing microalgae in deserts stands out as an emblematic example of how science and technology can collaborate with nature to sustainably feed a growing population.
Democratizing Agriculture: Beyond Water
In his presentation, Miguel Calatayud introduces us to a revolutionary vision of agriculture, addressing how innovation can serve as a catalyst for more inclusive and equitable food production.
The democratization of agriculture, according to Calatayud, involves bringing food production opportunities to regions and communities that have traditionally been marginalized within the global agricultural system. It refers to the implementation of technologies that allow cultivation in adverse conditions, such as the aforementioned cultivation of microalgae in deserts using saline water, and also to transform agriculture into a more accessible and sustainable activity for a wider diversity of producers.
Innovation for inclusion
Calatayud highlights how innovation, especially in the cultivation of species resistant to extreme conditions, can open new agricultural frontiers. In doing so, it expands the geographical areas suitable for agriculture and provides tools and knowledge to communities in desert regions or affected by climate change so that they can grow food and sustain their local economies. This agricultural inclusion promotes food security and sovereignty, allowing communities to produce what they need and reduce their dependence on costly and sometimes unsustainable imports.
The Future of Agriculture: Water Sustainability
Miguel Calatayud, in his in-depth discussion of the challenges and solutions for the agriculture of the future, places special emphasis on water sustainability. Water sustainability is not only a matter of conservation, but an imperative to guarantee food production in the present and for future generations.
Innovation and technology: keys to efficient water management
The adoption of advanced technologies, such as precision agriculture, drip irrigation, and smart irrigation systems, stands out as a critical step towards more sustainable agriculture. These technologies allow for more efficient use of water, reducing waste and maximizing productivity. Calatayud points out how incorporating big data and artificial intelligence into agricultural management can facilitate more accurate water distribution, ensuring that every drop is used as effectively as possible.
Water as a common good
In his vision of the future, Calatayud stresses the importance of recognising water as a common good that must be managed fairly and equitably. Water sustainability, therefore, also implies a social and ethical component, where access to water is considered a fundamental right for all, ensuring that communities, especially the most vulnerable, have the capacities to manage this resource in a sustainable way.
Towards a sustainable and resilient future
Calatayud’s presentation concludes with a call to action to adopt more sustainable and water-efficient agricultural practices. Water sustainability in agriculture is an essential step towards creating more resilient food systems, capable of adapting and thriving in the face of environmental and climate challenges. In this envisioned future, innovation, technology, and a global commitment to sustainable water management are critical to ensuring that agriculture continues to be a source of life and livelihood for humanity.
If you want to delve into the opportunities and challenges of agriculture and food, don’t miss the brief Smart Agriculture: the challenge of sustainable food.
You can also read articles about other presentations by experts participating in this Future Trends Forum:
Economic paradoxes in food security and long-term climate adaptation, with Gonzalo Delacámara.
Deciphering soil DNA: the importance of the microbiome in sustainable agriculture, with Adrián Ferrero.