AI-generated summary
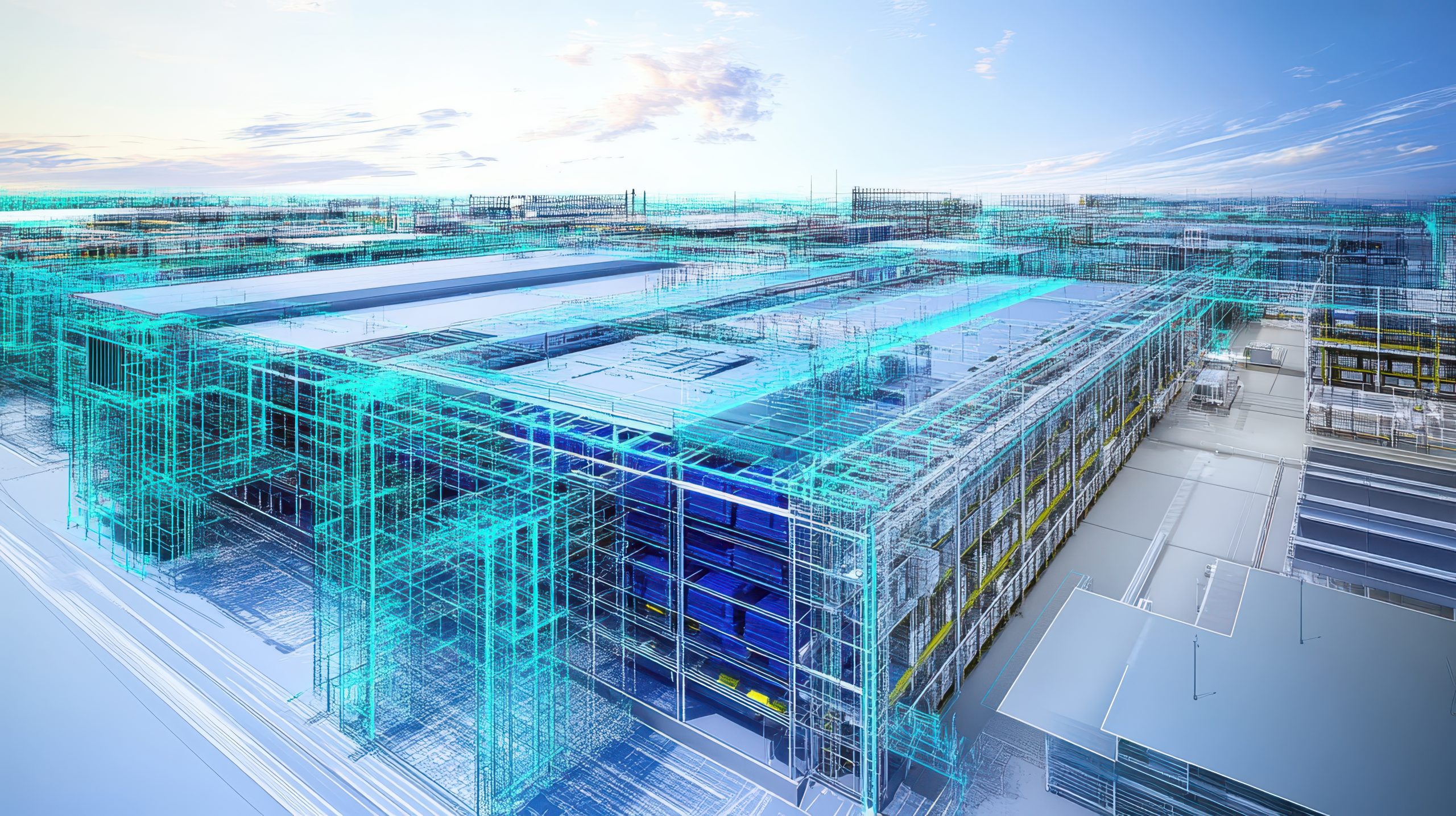
Digital twins have become a transformative technology in the digital era, enabling companies, cities, and organizations to create virtual replicas of physical objects, processes, or systems. This allows for real-time simulation, optimization, and predictive analysis, leading to more informed and efficient decision-making. Originating from concepts used by NASA in the 1970s and formally named in 2002, digital twins have evolved by integrating IoT, AI, machine learning, and big data analytics. Unlike traditional simulations, digital twins continuously process real-time data throughout the lifecycle of their physical counterparts, offering insights that support complex decisions and continuous improvements.
Their applications span diverse sectors: in manufacturing, digital twins facilitate predictive maintenance and production optimization; in energy, they enhance operational efficiency and environmental compliance; in healthcare, they support personalized treatment planning through detailed organ models. Smart cities use them for urban planning, resource management, and climate resilience, with examples including Amsterdam’s energy grid optimization and Barcelona’s urban accessibility simulations. The technology’s success relies heavily on AI and IoT integration, enabling faster, more accurate responses to dynamic conditions. However, challenges such as data privacy, security, and equitable access call for robust ethical and regulatory frameworks. With a rapidly growing market projected to reach $110.1 billion by 2028, digital twins are poised to become integral in addressing complex 21st-century challenges, driving smarter, more sustainable futures through responsible adoption.
Digital twins are revolutionizing the way companies, cities and organizations make decisions, optimizing processes before applying them in the physical world.
In the midst of the technological revolution, digital twins have established themselves as a tool that allows companies, cities and organizations to make more informed and efficient decisions. By creating virtual replicas of objects, processes, or physical systems, they actually make it easier to simulate scenarios, optimize processes, and predict outcomes before implementing real-world changes.
Although the term “digital twin” was coined by Michael Grieves in 2002, the underlying idea dates back to 1970, when NASA used simulations to save the Apollo 13 crew. Since then, the technology has evolved significantly, integrating advances in the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and analytics Big data to create dynamic and accurate models that reflect the behavior of their physical counterparts.
As a result, users can perform simulations and predictive analytics to anticipate problems, explore new opportunities, and support projects with greater awareness and objectivity than traditional methods. Unlike simple virtual simulations, focused on specific events or phenomena, digital twins span the entire life cycle of the physical object. The flow of real-time data is processed to extract valuable insights that generate insights, supporting complex decisions and continuous improvement of processes or products.
Applications in all areas
In the manufacturing sector, digital twins enable real-time monitoring of equipment and processes, facilitating predictive maintenance and reducing downtime. For example, BMW uses them to optimize its production lines, which has resulted in a 25% reduction in factory operations planning time.
In the energy arena, companies are adopting digital twins to improve operational efficiency and comply with environmental regulations. The implementation of this technology can lead to energy savings of up to 30% and a significant reduction in operating costs.
In healthcare, digital twins are revolutionizing personalized healthcare. By creating digital models of organs or body systems, healthcare professionals can simulate procedures, predict reactions to treatments, and optimize surgical interventions. A prominent example is the use of digital twins of the heart to improve the diagnosis and treatment of heart disease, integrating AI and extended reality algorithms for detailed visualization.
The Smart cities are also adopting digital twins to improve urban planning and climate resilience, enabling infrastructure simulation, efficient resource management, and proactive response to environmental challenges. For example, Amsterdam uses digital twins to optimize energy distribution and stabilize the local grid, while Palermo, Italy, employs digital spatial monitoring tools to manage and maintain drought-affected green spaces.
In Spain, several cities are adopting digital twins to improve urban planning and sustainability. Barcelona is using a model developed by the Barcelona Supercomputing Center to assess whether the city meets the “15-minute city” criteria. This program allows simulating urban scenarios and analyzing accessibility to essential services within a radius of 15 minutes on foot or by bicycle.
The effectiveness of digital twins is highly dependent on the integration of technologies such as AI and IoT. Specifically, IoT sensors collect data in real time, which is then analyzed by AI algorithms to identify patterns, predict failures, and suggest improvements. This synergy allows for faster and more accurate decision-making, adapting to changes in the environment and optimizing the performance of complex systems.
Ethical Challenges and Considerations
Despite their benefits, implementing digital twins poses significant challenges. The collection and analysis of large volumes of data raises concerns about privacy and information security. In addition, reliance on advanced technologies can exacerbate inequalities if equitable access to these tools is not ensured. Therefore, it is essential to establish regulatory and ethical frameworks that guide responsible use, ensuring that the adoption of these models benefits society as a whole and not just privileged sectors.
However, the The global market is experiencing exponential growth and is expected to reach $110.1 billion by 2028, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 61.3% since 2023. It is therefore quite possible that in the future digital twins will become even more integrated into our lives, from the From the personalization of medical treatments to the management of entire cities, and their ability to simulate and predict complex scenarios makes them an invaluable tool to meet the challenges of the 21st century.
Digital twins represent a convergence of technologies that are redefining the way we interact with the physical world. By providing a platform for real-time simulation and analysis, they enable organizations to anticipate problems, optimize processes, and make more informed decisions. As this technology continues to evolve, its responsible and ethical adoption will be key to maximizing its benefits and minimizing risks, ensuring a smarter and more sustainable future for all.