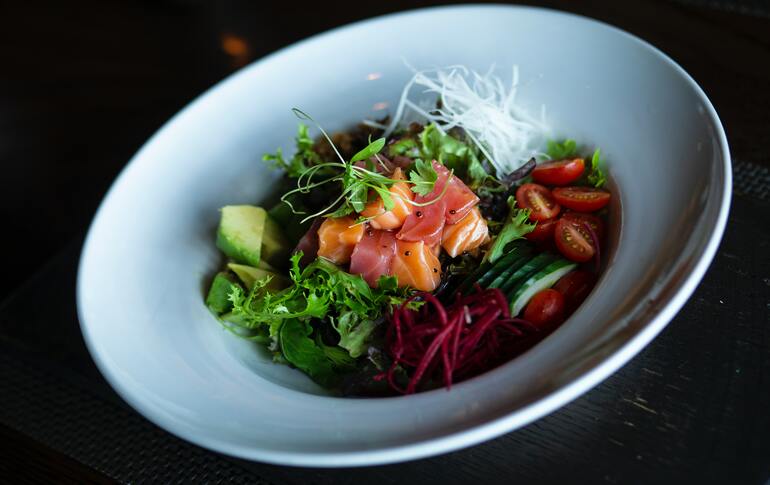
Cellular agriculture is based on taking the most elementary units of life of living beings, cells, and cultivating them to turn them into true animal products.
How can the sustainability of the global food system provide healthy nutrition to the entire world population in the next fifteen years? The key is in cultured proteins.
On June 3 and 4, the XXXIV Future Trends Forum was held: “The food of the future”, where more than thirty world experts in the field met, this time virtually, to answer and propose actions to this question.
Among other issues, innovations in raw materials that could change the way we eat were addressed, with a focus on so-called cellular agriculture.
We are not talking about vegetarian meat or fish, nor are we talking about using genetic mutations. Cellular agriculture proposes the production of animal products in a sustainable way, in vitro, by cultivating animal tissues.
Lou Cooperhouse, President and CEO of BlueNalu, explains what the creation process is in cellular agriculture: the first step is to take some cells from an animal’s muscle. The cells that are taken are called myosatellite cells, which are the stem cells of muscles. The function of these stem cells within the animal is to create new muscle tissue when the muscle is injured. This inherent property of stem cells is what is used to make cultured meat or cultured fish.
Cooperhouse tells us that the acceptance by consumers and chefs is being very good in the first tasting tests they are doing with their farmed fish.
Why cultured protein cell farming?
In the case of BlueNalu, focused on the creation of fish proteins, it seems clear that overfishing, illegal fishing, ocean acidification, rising ocean temperatures, pollutants, viruses, etc. are drastically reducing the world’s supplies of seafood and endangering its very survival.
Cellular agriculture tries to respond to the challenge of feeding the population correctly without incurring the enormous economic and environmental costs involved in obtaining proteins of animal origin:
- Healthier population through safer and perfectly controlled products without antibiotics or risk of foodborne diseases.
- Respect for animal life in the production of animal products without animal suffering. To facilitate a sustainable future that reduces our use of natural resources without calling for massive behavioural change.
For the expert, there are stillchallenges to overcome before this type of food is massively marketed:
- Achieve economies of scale. Today, it still costs a few euros to make a portion of cultured meat or fish. The objective is to reach a cost of a few tens of euro cents.
- Strong need for capital to build the necessary factories.
- Overcoming regulations. Given that, in the case of the company represented by our expert, no genetic manipulation is carried out, the regulatory procedures are only those corresponding to novel foods in the case of Europe, through the European Food Safety Agency. In the case of the U.S., it is somewhat more complicated because several state agencies such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the Department of Agriculture (USDA) are involved, which must coordinate. In any case, the expert is optimistic about the regulation of its products.
You can download a summary of what was discussed at the Future Trends Forum “The Food of the Future”, and access the videos of the experts who participated, by clicking here. You will learn more about the Foodtech revolution.